Post: Generate CyberArk PAS REST API Authz Tokens Using Java Spring-Boot
CyberArk supports many different authentication methods for interactive logins for privileged end users and administrators. Similarly, in many situations there is a need for administrators to interact with CyberArk components to perform their day to day activities, onboarding accounts and creating vault entities like Safe, Platform etc.
As we know CyberArk provides rich set of REST capabilities with well-defined Swagger. This will make administrators life easier to make automation scripts and day to management of the PAM solution. I’ve been observing CyberArk’s Marketplace for years and there are limited options for SME’s and administrators since most of the sample REST scripts are developed using Powershell. In this post Im going explain how we can leverage java to make REST calls to CyberArk PAM Web Service.
In this article I’m going to use Java and Spring-Boot to make REST calls to generate API credentials (which will then be used for different operations like Add Account, Delete Account and Add Safe etc).
Pre-Requisites:
Make sure your workstation/ Laptop installed with the below tools for this simple exercise.
• JDK 1.8 or more
• Eclipse (IDE for java & Spring boot)
• Maven (Build tool)
In addition, we need to have a service account from CyberArk which will be used as a logon account to get the authorization credentials.
I’ve created simple Spring-Boot project (cyberark_pam_rest_authentication) in Eclipse and project structure is as follows:
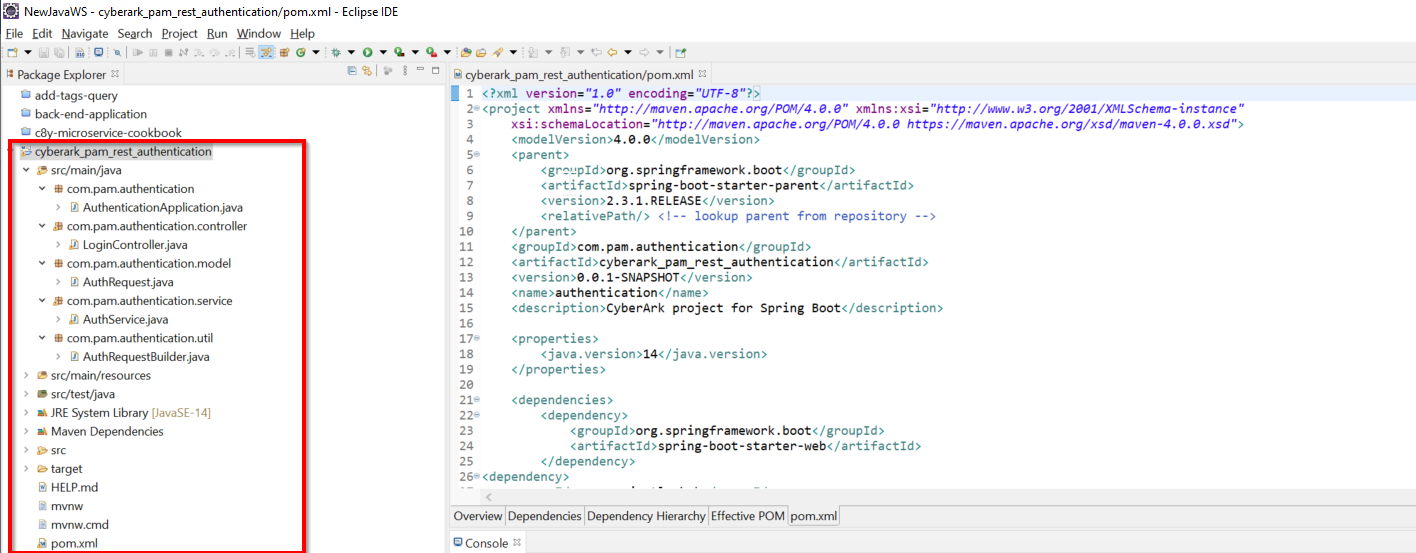
The main class resides in the AuthenticationApplication.java and it will be starting point for any spring boot services.
package com.pam.authentication;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class AuthenticationApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(AuthenticationApplication.class, args);
}
}
The AuthRequest.java is a simple POJO class which is nothing but a model class in the MVC framework.
package com.pam.authentication.model;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
@Getter
@Setter
public class AuthRequest {
private String username;
private String password;
private String newpassword;
private String type;
private String additionalInfo;
private Boolean secureMode;
private String concurrentSession;
}
The AuthRequestBuilder.java class will be used to set the user name and password for service authentications.
package com.pam.authentication.util;
import com.pam.authentication.model.AuthRequest;
public class AuthRequestBuilder {
public AuthRequest buildAuthRequest(String username, String password)
{
AuthRequest authReq = new AuthRequest();
authReq.setUsername(username);
authReq.setPassword(password);
authReq.setConcurrentSession("false");
authReq.setSecureMode(false);
return authReq;
}
}
Class AuthService.Java is main service class where spring boot constructs the request module and post REST request to
CyberArk PVWA URL.
package com.pam.authentication.service;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URI;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.Base64;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.http.HttpEntity;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.HttpMethod;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import com.pam.authentication.model.AuthRequest;
import com.pam.authentication.util.AuthRequestBuilder;
import com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.security.utils.Base64;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
@Service
public class AuthService {
@Value("${application.logon.url}")
private String access_token_url;
@Value("${application.logout.url}")
private String logOff_url;
@Value("${auth.username}")
private String username;
@Value("${auth.pass}")
private String password;
public ResponseEntity<String> getAccessToken() throws IOException
{
AuthRequestBuilder auth=new AuthRequestBuilder();
AuthRequest alRequest = auth.buildAuthRequest(username, password);
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
String jsonStr = mapper.writeValueAsString(alRequest);
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON);
HttpEntity<String> request = new HttpEntity<String>(jsonStr,headers);
ResponseEntity<String> response= restTemplate.postForEntity(access_token_url, request,String.class);
System.out.println("New Authentication Response ");
String authorizationToken=response.getBody().toString();
HttpHeaders headers1 = new HttpHeaders();
authorizationToken=authorizationToken.substring(1, authorizationToken.length()-1);
System.out.println("Token : "+authorizationToken);
headers1.setAccept(Collections.singletonList(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON));
headers1.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON);
headers1.add("User-Agent", "Spring's RestTemplate" );
headers1.add("Authorization", authorizationToken);
HttpEntity<String> requestEntity = new HttpEntity<String>(null,headers1);
ResponseEntity<String> response1 = restTemplate.exchange(logOff_url, HttpMethod.POST, requestEntity, String.class);
System.out.println("Log Off Response Code : " +response1.getStatusCodeValue();
System.out.println("Log off Response : "+response1.getBody());
return response1;
}
}
In general use case once we get the authorization token which then will be used for subsequent operation like safe creation, modification etc. when the required operation is completed, we need to logout properly.
Class AuthService.Java is main service calss where spring boot constructs the request module and post REST request to
CyberArk PVWA URL.
For simplicity the REST service is invoked via browser and you can also use Postman too to invoke the same.

If there is no error you will get the authorization when you execute/run the code through Eclipse ..
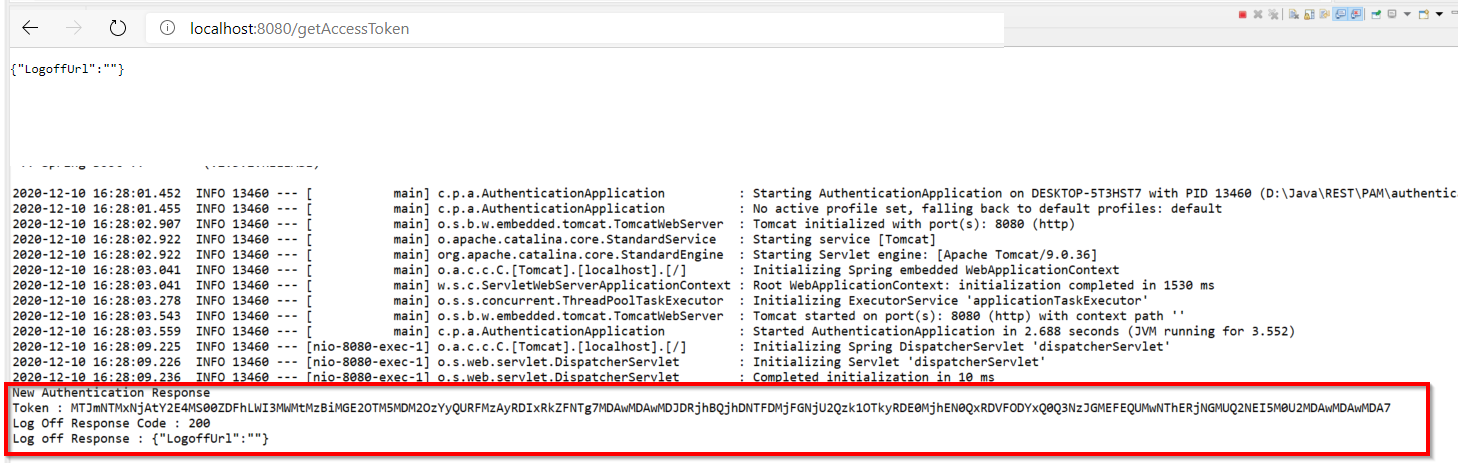
The entire project is at the github and you can access them at Nirmal’s GitHub repo. For any further queries. please reach out to me.
Summary
As of today, I never come across any Java Spring-Boot examples for CyberArk REST API calls. Its recommended to follow steps and setup your project accordingly. In the subsequent post I’m planning to cover more complex scenarios. Stay tuned!!
